What are Growth Hormones and Why Are They Used in Agriculture?
Synthetic plant growth promoters are designed to mimic natural growth hormones, which occur in living organisms to regulate cell growth, development, and metabolism.
In humans and animals, growth hormones (GH) are produced by the pituitary gland and play a crucial role in stimulating cell and bone growth, muscle development, and regulating energy metabolism.
In plants, growth hormones, known as phytohormones or plant growth regulators play a crucial role in regulating various physiological processes. These hormones help plants grow, develop and respond to their environment.
Some key functions of Synthetic Plant Growth Promoters include:
- Growth promotion and development of roots, shoots and branching
- Fruit formation, growth and ripening
- Helping plants respond to environmental stress
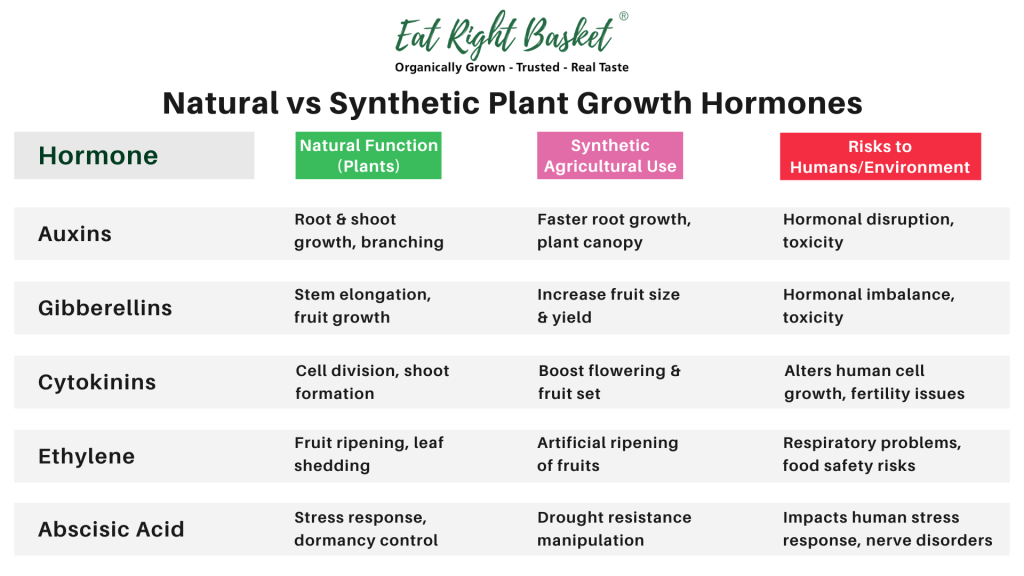
Auxins, Gibberellins, Cytokinins, Ethylene and Abscissic Acid all work in tandem to ensure naturally healthy and timely growth, flowering, and fruiting.
Synthetic Growth Hormones in Agriculture: The Shift from Nature to Profits
All is well when natural growth hormones are working in their natural systems. The real problem starts when vested interests in science and technology mimic nature to exploit it for reaping profits.
Today, all of the above mentioned plant hormones are being widely used in agriculture for enhanced production:
- Rapid growth of plants
- Stronger roots and denser canopy
- Larger number of flowers and improved flower health
- Bigger fruit size and faster ripening
Beyond crops, growth promoters are also rampant in the meat, poultry and dairy industries, where animals are fed hormones for faster growth, higher weight gain and increased milk production.
Is It Safe to Use Synthetic Plant Growth Promoters in Food Production?
Several studies and research globally indicate that although use of these hormones in agriculture production may improve plant health, unregulated and long-term application by farmers can lead to hormonal imbalances in humans and animals feeding on such produce.
This remains a subject requiring long-term research due to the complexity of hormones and their widespread use.
Impact of Synthetic Plant Growth Promoters on Human Health
Some complications that may arise due to regular consumption of hormone-treated food include:
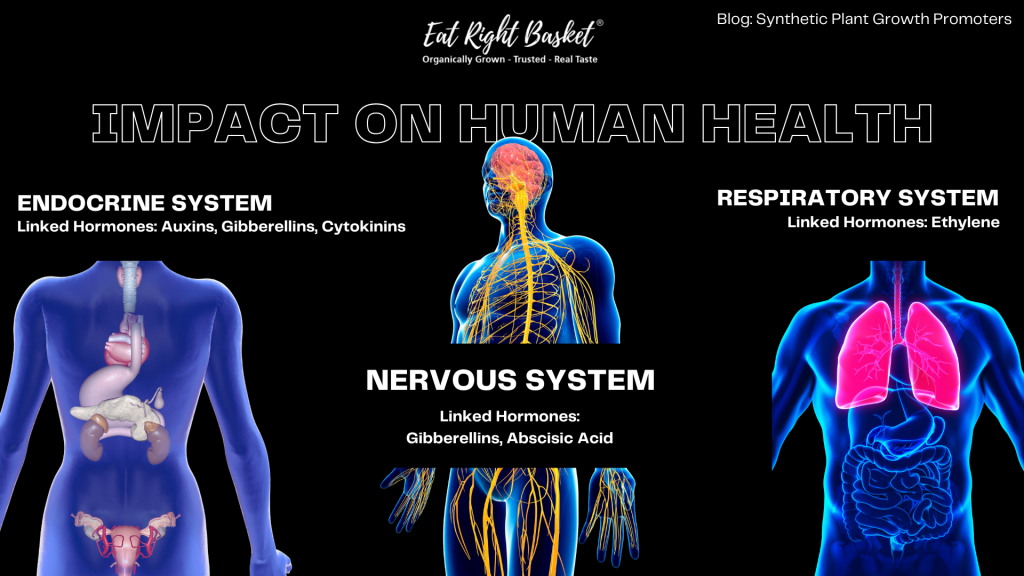
- Auxins: Linked to hormonal disruption and potential toxicity
- Gibberellins: May cause hormonal imbalances and toxicity
- Cytokinins: Potential impacts on human cell growth and development
- Abscisic Acid: May affect stress responses and hormone regulation
- Ethylene: Can impact respiratory health and plant-animal interactions
Exposure to Synthetic Plant Growth Promoters in food can disrupt natural hormone balances in humans. Some studies suggest potential links to cancer risk. Overuse in farming may also contribute to antibiotic resistance.
Impact on the Environment
Excessive use of synthetic growth hormones in agriculture harms ecosystems as well:
- Water pollution: Contamination of rivers and water bodies, affecting aquatic life
- Soil degradation: Damage to soil health and fertility
- Biodiversity loss: Harm to non-target species and ecosystems
Regulations in India: Where Do We Stand?
The Government of India has yet to take legal action on the application of synthetic plant growth promoters in agriculture. While guidelines exist, they are difficult to enforce, given farmer ignorance and pressure to maximize yields.
The market for such chemicals in India is steadily growing, estimated to rise by 8.5% by 2030.
Easy Availability of Synthetic Growth Hormones in India
Synthetic plant growth regulators are easily available through:
- Online marketplaces
- Agricultural supply stores
- Imported brands
Commercial marketing has ensured penetration into rural markets, with free delivery across India making them even more accessible.
The Risk Factor: What We Don’t Yet Know
The impact of synthetic growth hormones on long-term human and animal health remains under-researched.
While not much empirical evidence exists, increasing cases of hormonal imbalance, nerve disorders, and reproductive issues are being linked to rising use of these chemicals in farming and food industries.
How to Eliminate Synthetic Hormones from Your Food Plate
In absence of strict government regulation, consumers must take responsibility. You can reduce exposure by:
- Choosing organic produce → Fruits, vegetables, grains
- Checking labels → Look for certifications like organic, natural, residue-free
- Supporting sustainable agriculture
- Preferring home-cooked meals over processed food
- Staying informed about plant growth promoters and health risks
- Advocating for safe farming practices
Eat Right and Stay Healthy!
References Used for the Blog
IndustryARC – India Plant Growth Regulators Market
AgriFarming – Plant Growth Promoters




